In today’s digital world, security is a top priority for websites, especially those handling sensitive information like personal data or financial transactions. One crucial aspect of online security is the use of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates.
These digital certificates function like passports for websites, verifying their identity and enabling a secure encrypted connection between a user’s web browser and the server. This encryption scrambles the data being exchanged, making it unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it.
Imagine it like whispering a secret code between two people – even if someone eavesdrops, they won’t be able to understand the message.
What is SSL?
SSL is an abbreviation for Secure Sockets Layer, a protocol that establishes a secure and encrypted communication channel between a web browser and a website. It ensures that the data transmitted over this connection remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access or interception.
This encryption helps protect sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal data, and credit card numbers, from being intercepted by hackers or other malicious actors.
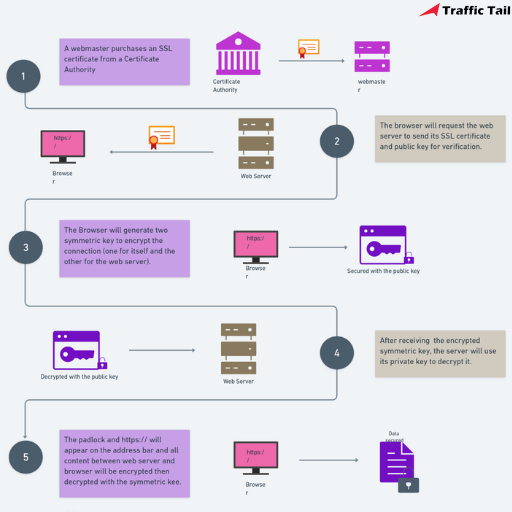
SSL uses a combination of encryption keys to secure the data transmitted between the browser and the website. When you visit a website with an SSL certificate, your browser and the website server engage in a process called an “SSL handshake.” During this handshake, the server provides its SSL certificate, which contains a public key used for encryption.
Also Read: Best Ecommerce Payment Gateway For Your Business
How Does SSL Relate to HTTPS?
You may have noticed that some website addresses start with “http://” while others begin with “https://.” The “s” in “https” stands for “secure,” and it indicates that the website is using an SSL certificate to encrypt the connection.
Websites without an SSL certificate will use the standard “http” protocol, which means that any data transmitted between the browser and the server is sent in plain text. This makes it vulnerable to interception and potential data breaches.
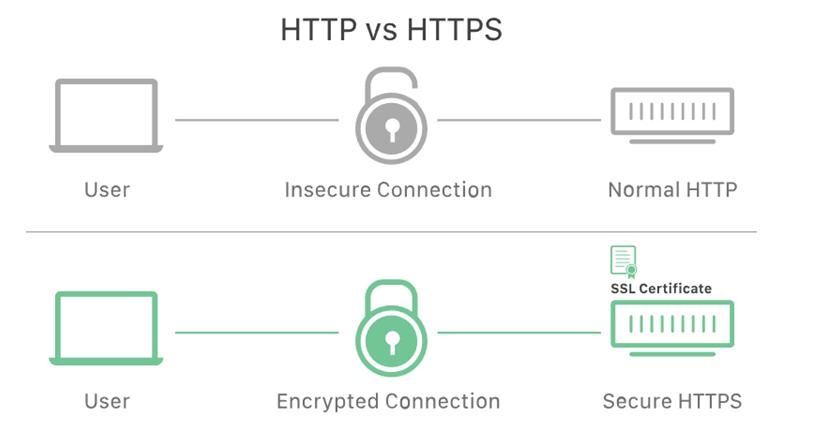
On the other hand, websites that use “https” have implemented an SSL certificate, ensuring that all data transmitted is encrypted and secure. Most modern web browsers will display a padlock icon or a “Secure” label in the address bar when visiting a website using HTTPS, indicating that the connection is secure.
Why is SSL Important?
SSL is crucial for any website that handles sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal data, or financial transactions. Here are some key reasons why SSL is important:
- Data encryption : SSL encrypts all data transmitted between the user’s browser and the website, preventing unauthorized parties from intercepting and reading the information.
- Authentication: SSL certificates verify the identity of the website, ensuring that users are communicating with the legitimate website and not an impersonator.
- Search engine optimization (SEO): Google and other search engines prioritize websites with SSL certificates in their search rankings, as they value providing a secure online experience for users.
- Compliance: Certain industries and regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for e-commerce websites, require the use of SSL certificates to ensure the secure handling of sensitive data.
Types of SSL Certificates
SSL certificates come in different types, each offering varying levels of validation and security. There are three primary categories of SSL certificates:
1. Domain Validation (DV) SSL Certificates: These are the most basic and affordable SSL certificates. They provide encryption but only validate the domain ownership, not the identity of the website owner.
2. Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates: These certificates require verification of the website owner’s organization details, such as the company name and address. They offer a higher level of trust and credibility compared to DV certificates.
3. Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates: EV certificates undergo the most rigorous validation process, requiring extensive verification of the organization’s legal and operational existence. They provide the highest level of trust and security, and most modern browsers will display a green address bar or a company name to indicate the use of an EV SSL certificate.
SSL certificates can also be grouped according to the number of domains or websites they secure:
4. Single-domain SSL certificates: These certificates secure only one domain and cannot be used for subdomains.
5. Wildcard SSL certificates: Provide encryption for a primary domain as well as all subdomains that fall under that main domain.
6. Multi-domain SSL certificates: These certificates secure multiple domains and their subdomains.
How do I install an SSL certificate on your Website?
Installing an SSL certificate on your website is a straightforward process, but it may vary slightly depending on your web hosting provider and the type of server you’re using. Here’s a general step-by-step guide:

- Choose a reputable SSL certificate provider: Select a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) to purchase your SSL certificate from, such as Let’s Encrypt, DigiCert, or Comodo.
- Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR): You’ll need to generate a CSR, which contains information about your domain and organization. This can typically be done through your web hosting control panel or server software (e.g., cPanel, Apache, or IIS).
- Purchase and validate your SSL certificate: After generating the CSR, you’ll need to purchase the SSL certificate from your chosen provider. The provider will then validate your information and issue the SSL certificate.
- Install the SSL certificate: Once you receive the SSL certificate, you’ll need to install it on your web server. This process may vary depending on your hosting provider or server software, but most providers offer step-by-step instructions or automatic installation tools.
- Configure your website for HTTPS: After installing the SSL certificate, you’ll need to configure your website to use the HTTPS protocol. This typically involves updating your website’s URLs and enforcing HTTPS through server settings or website code.
If you’re using a WordPress website, you can easily enable SSL by installing a plugin like “Really Simple SSL” or by manually updating your WordPress settings to use HTTPS.
Conclusion
SSL/TLS and HTTPS are important for keeping internet communication safe and private. Certificates link real identities to special codes (key pairs) that encrypt data. When you visit a website, your browser and the website’s server follow the SSL/TLS process to set up an encrypted connection.
Website certificates, issued by trusted companies like DigiCert or Comodo, verify the website’s identity and act as a digital seal of approval. This verification ensures you’re not interacting with a fake website designed to steal your information.
Understanding these concepts is vital for online activities like online banking, where sensitive financial data is exchanged. By utilizing SSL/TLS and HTTPS, websites not only protect your information but also build trust with their users. After all, who wants to shop at a store with a broken lock on the door?
FAQ’s
1. What is SSL email?
SSL email, also known as encrypted email, scrambles the content of your emails using encryption technology (SSL/TLS) to ensure it stays confidential during transmission. This is especially important for emails containing sensitive information like financial data or personal details.
2. How does it work?
Imagine an email as a letter and SSL/TLS as a fancy lock. The sender’s email client uses a key to scramble the email content (locking the letter). The recipient’s email client then uses another key to unlock it (reading the letter). These keys make sure only the intended recipient can access the message.
3. What is an SSL connection?
An SSL connection is a secure connection between two devices on the internet. It uses SSL/TLS to encrypt data being exchanged, protecting it from eavesdroppers or tampering. You’ll often see a padlock symbol in your browser address bar when using a secure SSL connection.
4. What is an SSL error on iPhone?
SSL errors on iPhones can happen for various reasons, like outdated software, issues with the website’s SSL certificate, or problems with your internet connection. These errors prevent your iPhone from establishing a secure connection with the website.
5. What is an SSL error?
An SSL error is a general term for any problem encountered while creating an SSL connection. It can happen on various devices, including iPhones, and can indicate different underlying issues.






